Decision Making Framework Supported By Knowledge
Management Activities
Marwan Hesham Noman, Azira Abd Aziz, Multimedia
University, Malaysia
ABSTRACT:
Managerial positions have been known as the most eligible positions for decision making. All organizations are entitled to have a decision every day and be responsible of its results. This research is going to help the managers’ managerial thinking by providing a new framework of decision making techniques. The techniques are available through books, articles and journals, but the key is how the organizations combine these methods into one framework and get mixture of decision making methods. There are two focuses of knowledge management enablers in this study, which are culture and infrastructure. Most of decision making failure opportunities are related to people in the first phase which is part from infrastructure, and culture in the second phase since company and country regulations will play an important role toward decision making. The study will be analyzing those behaviors based on the resulted inputs from the collected data. In the findings area, objectively the results should come out to show the comparison strategy between the exciting frameworks in the literature review and the data collected. This study will report the decision strengths and weaknesses derived from questionnaires and interviews. Semantic analysis will take place to compare the results with the existing mechanisms found in the literature review.
Keywords: Decision making models, Cultural factors,
Industrial factors, Technology tools, Knowledge sharing, Knowledge factors
1.
Introduction
Nowadays people make decisions everyday without even realizing it. They don’t take fully notice on how these decisions are going to affect their life/ business functionality sooner or later. All top and middle managers are holding the authority to announce the decision and be responsible of its performance as well. That’s why decision making action should be endured under the knowledge management environment to be used as a supporter to enable the knowledge management process. An individual’s problem solving and decision making capability is limited by the knowledge available. Having available knowledge to decision makers is crucial for improving individual and organizational performance. Therefore, the decision-making oriented approach is a valid way of identifying knowledge requirements (Kim et al, 2004). By looking at the Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom continuum Figure 1, most people can realize that it is designed and structured perfectly to support the decision making process. It looks like a developing of an idea, or it seems as the sequence of stages to build your decision. Bellinger (2001) has illustrated the progression as followed ‘A piece of information is an aggregation of data relating to specific natural or social entity or entities that conveys the meaning, and stimulates understanding and action through its recognizable pattern’ (United Nations, 2001: 3).
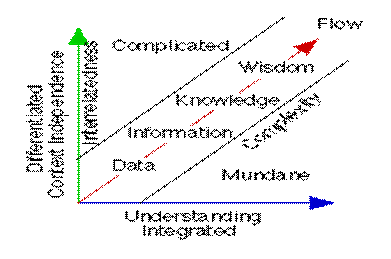
Figure 1:
Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom Continuum. (Bellinger,
2001)
1.1. Problem
Statement
The main issue is how organizations will have the ability of using a new technique of decision making. Some executives are following and adding a value to their personal knowledge management and they aren’t aware of it. Top Management should distinguish whether the decision can be made by a person or a group, and both of them should be practiced through the organization activities to ensure the familiarity of the skill.
1.2. Decision
Making and Knowledge Management
Haroon (2007) has called for a recap of knowledge management into decision making, ‘It is concerned with the representation and processing of knowledge by humans, machines, organizations and societies’ (Haroon, 2007: 7). It was stated the DSS (Decision Support System) will not substitute humans no matter how these systems will go so far. DSS is implemented by most of the international companies to help assisting the employees and analyzing the situations. ‘Computers will never be substitutes for humans in complex decision situations. But they can surely lend support to decision makers in helping us to make more humane decisions’ (Haroon, 2007: 12).
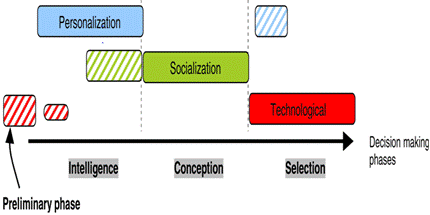
Figure 2:
Impact Of KM Strategies On Decision Making. (Haroon, 2007)
1.3. Research
Questions
The research will focus on many questions, and these questions will be explored deeply through the development stages:
· How the executives from different industries and organizations’ cultures go through the decision making process.
· What are the factors that managers are taking in consideration in order to process a decision.
· How knowledge management activities can enhance the decision making process.
1.4 . Research Objectives
There are no specific objectives to achieve into this research. But the main concern is to find a solution of the mentioned research questions, there will be an investigation and observation on how the resulted decisions are affected by knowledge management enablers such as Infrastructure, Culture and Technology. But the research will be concentrating more on the culture and infrastructure factors, because people and culture play the most influenced role towards decision making process. The people are build from emotions, which means their decisions will be directly affected by the working pressures and operational environment. ‘The idea that our decisions and judgments are not always colored by conscious reasoning processes’ (Cremer et al, 2010: 5). In addition, Akhter (2010) has also explained how emotions can lead to critical decisions ‘Emotions play a vital role in making any decision. It has been observed that hot tempered person takes irrational decisions’ (Akhter, 2010).
Even the culture will be still controlling the process of decision making. The organization or country will be the top of the ranking hence the country regulations and organizations’ cultures will be alternating the idea of decision making possibility. Markman (2010) has mentioned the difference between individualism and collectivism. Respectively, East Asian cultures are more to be collectivism or group oriented nation. On the other hand, The Western culture is clearly individualism. ‘European Americans, for example, are generally influenced by the positive consequences of a decision, whereas Asians appear to be more influenced by the negative consequences that may occur due to a decision or line of action’ (Briely, 2007).
This study will also investigate on the factors that usually affect decision making process. Actually the factors are almost known such as business nature and position responsibilities. But the research will go deeper to know why these factors can a play a role during making the decision. It will analyze how the practice of knowledge management activities can minimize the factors’ contribution in order to get decision with full commitment. The culture of the country and organization will also have an important affection. Therefore, this research is designed to have an overview about the culture perspectives through decision making, and how country regulations may affect knowledge management activities. Obviously, the culture of organization will draw an image of how the decision is made, and that’s why this study tries to explain how organization cultures can enhance decision making process by practicing knowledge management activities. At the same time, the organization culture will still follow the country or community regulations.
2. Related
Literature Review
In this section, there will be a review of the existing frameworks which are related to decision making methods. The section will explain the details of each adopted framework in order to cope it with the current research. The existing researches about the decisions issue will help analyzing the approach of knowledge management process through decision activities.
2.1. Business
Decision-Making
First, figuring out the objectives behind the decision, which means decision makers must know their goals first to get the green light to be involved in the decision process. Next, the colleting of information available data will take a place, and will be followed by analyzing these information and data. Bowett (2009) has suggested two elements to support the collecting and analyzing steps; he recommends that we need to look for very relevant and updated data so the decision will be built based on up-to-date information. He suggests a method for the analyzing process, ‘A very large spread-sheet can be used to hold all the known information about, say, pricing and the effects of pricing on profits’ (Bowett, 2009). Now, it comes to the most important step which is making a decision based on the collected information. He has defined the secondary steps of making a decision as several possible solutions, but to be analyzed and evaluated to choose the best solution. Therefore the decision will be needed to be discussed among the team or the organization by communication. Here is the connection between decision making and knowledge management has been related by knowledge sharing method. Implementation of the taken decision and evaluating it will be the last two steps of the process.

Figure
3: Business Decision-Making Process.
(Bowett, 2009)
2.2. Systematic
Decision-Making Approach
Mind Tools has suggested the systematic approach for decision making, and it is really dedicated to be adopted in the knowledge management environment. First it discusses some of the common issues that related to decision making, Uncertainty, Complexity, Alternatives, Interpersonal Issues and risk consequences. ‘A logical and systematic decision-making process helps you address the critical elements that result in a good decision’ (MindTools, 2010). The steps are:
- Create a constructive environment.
- Generate good alternatives.
- Explore these alternatives.
- Choose the best alternative.
- Check your decision.
- Communicate your decision, and take action (MindTools, 2010).
2.3. CCVC
Decision-Making Methods
Patterson et al (2002) have proposed 4 decision making techniques, which are Command, Consult, Vote and Consensus. Patterson et al (2002) suggested that command technique is used when there is no involvement. In other words, they meant that command is used where there is force, or just follow the leader. In both cases there is no involvement. Consultation will happen when a leader is looking for suggesting assistance from the members. Members should have the action of brainstorming during this technique; the leader will have to listen to all opinions, ideas, suggestion and notes. At the end, the leader will have to make a decision based on the previous inputs. Voting is a great strategy as well since it grabs members’ points. It is very important to use voting when the discussion between members reach to nowhere, the leader will need to save time and call for voting to make a decision. But it has some disadvantages such as ignoring people opinions; in this case the consensus technique is required. Consensus is the most effective towards decision making, but at the same time it is the hardest to occur. Because reaching to consensus point means satisfying all the minds, which is rarely available (Patterson et al, 2002).
2.4. Scientific
Decision-Making Framework
Organization environment seems to be an affective factor towards decision making process. Health Canada (2010) has established a scientific decision making approach in order to cope with the health policies. ‘Health Canada's Decision Making Framework is a process for identifying and managing risks to health. These risks may arise from diseases, hazardous substances, food, medical devices, drugs, tobacco and consumer products’ (Health Canada, 2010). The framework focuses on 3 main issues Issue Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Management.
Identifying the issues in the scientific framework equals to identifying the objectives in the managerial approach. It is still the same concept, but the different factor is environment. The next step issue is risk assessment which is similar to analyze the decision to figure out the benefits behind it. After that, it will go through risk management which includes several processes such as implementing a strategy, controlling a process and evaluating the results. Figure 4 shows the involved steps of the scientific decision-making framework
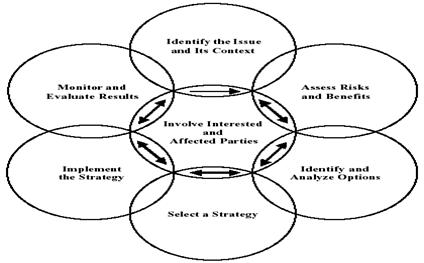
Figure
4: Scientific Decision-Making
Framework. (Health Canada, 2010)
2.5. Strategic
Decision-Making Framework
As mentioned before, the organization environment will still play an important role to enhance the decision making mode. A strategic decision making framework was suggested by information-technology research group which is a part of a community called Information Edge (InfoEdge, 2006). The group has decided the framework to be contained of four steps:
1- Setting Strategic Goals.
2- Performing a Budget Analysis.
3- Identifying Options.
4- Prioritizing the Project.
2.6. Team
Decision-Making Methods
Johnson et al (1993) have proposed several team decision making methods. They are some positive and some negative methods as well. Actually there is decision made based on individuality, but leaders sometimes make a mistake by ignoring members’ contribution which may reflect the effort. A brief of each of the methods suggested by Johnson et al (1993) will be explained as below.
Method 1: Decision without
Group Discussion
The decision built by the leader! That is the first method of group decision making. Basically, the group members are not involved in the decision at all since there is no discussion. It is similar like the command factor in CCVC method. Team members will not be aware of the resulted decision, plus it shows how there is no group interaction and commitment which is not supportive for knowledge management environment (Johnson et al, 1993).
Method 2: Decision by Experts
Experts will be the main function in this method, because some of the decisions will require some area of expertise. That’s why the leader sill needs to let the experts look into the issue and make the decision as well. But members may not understand the reasons behind the decision established by those experts, plus there is no group interaction as well since the focus was on the experts (Johnson et al, 1993).
Method 3: Decision by Averaging Individuals’
opinions
The leader will still have the final decision, but he will be asking opinions and ideas from the group members. This method grabs all the members into discussing their points of views, but not yet to be considered group interaction process. It may rise conflicting hence some of the members’ ideas will be just noticed and considered (Johnson et al, 1993).
Method 4: Decision Made by Authority
The team leader will be consulting all the members’ opinions and ideas. But at the end, the leader will be the only one who has the authority to establish the decision based on the member’s inputs. This method is very common nowadays among organizations, but actually it all depends on the organization nature as mentioned earlier. Some of the members will feel invaluable since their opinions weren’t taken into action (Johnson et al, 1993).
Method 5: Decision Made by Minority
‘A minority of the team, two or more members who constitute less than 50% of the team, make the team’s decision’ (Johnson et al, 1993: 120-140). This is a very rare method used in the executive and temporary committees.
Method 6: Decision Made by Majority
This method is exactly the opposite of the minority method. The majority voting will be considered here to compromise the issue. But the issue is that always ignore the minority opinions and there is no full group interaction. Because the decision will be considered successfully as long as more than fifty percent of the team agrees (Johnson et al, 1993).
Method 7: Decision Made by Consensus
It is better to call this method ‘Collective Decision’, because it ensures the acceptance by all the members. In result, it will load the commitment factor into the members’ willingness. It is very time consuming since the leader will try his/her strategy to get the acceptance from all the members (Johnson et al, 1993).
2.7.
Organization Culture and Industry Factors
This research is going to investigate on decision making models based on two perspectives; organization culture and industry. Organizations culture (OC) includes its determinants such policies, leadership style, managerial values, organization size and structure. All these factors can reflect the image of the organization culture; therefore the decision making process is affected by the organization culture. Hilton (2008) has explained how these determinants can play a role to structure and form the culture of the organization. ‘Note that OC is not influenced by factors existing within the organization only’ (Hilton, 2008). Hilton has also differentiated the situations between small and large companies, when Hilton explained the environment for companies as follow ‘In a small sized organization it is much easier to foster a climate for creativity and innovation or to establish a participative king of management’ (Hilton, 2008). Hilton meant that small companies are suitable for managerial style to support the creativity and innovation in order to grow up the company in the early stages. But when it comes to the large companies, Hilton stated ‘In a large organization it is easier to have a more authoritative kind of management with stress on vertical distribution of responsibilities’ (Hilton, 2008). So the authorization process is very important for the large companies in order to control the process and productivity of business units. The business nature of the organization can sometimes affect decision making process. Business nature of the organization indicates the industry that organization is participating in, therefore companies from different industries will require different decision making methods and techniques. For example, Heath Canada (2010) has establishes its own decision making framework to practice it during the health and science industry. ‘Health Canada's Decision Making Framework is a process for identifying and managing risks to health. These risks may arise from diseases, hazardous substances, food, medical devices, drugs, tobacco and consumer products’ (Health Canada, 2010).
2.8. Knowledge
Management Role towards Decision Making
Many people will think what the connection between knowledge management and decision making is. Actually there is a very serious affective connection that knowledge management is a very good factor of environment to support the decision making. It might sound a bit confused but actually knowledge management activities will lead us to be involved in hiring and firing employees. It also encourages use to use the organizational learning methods which are followed by knowledge sharing. McInerney (2005) has highlighted a point of quickness of decision making. It is knows that decisions will go through discussions, meetings and voting methods, but what if the decisions need to be quick?
McInerney (2005) has given an example or urgent cases, such as ‘A job search is completed, and the chosen candidate calls to say he cannot start the job for 6 months. Can he still have the job?’ (McInerney, 2005: 16). There is evidence that many, if not most decisions are made very quickly. Since many of our decisions are made very quick and without thinking. Knowledge sharing is very suitable to start making your decision with a convenience manner. Whenever you share your ideas, points and suggestions with the members; that might make valuable element to the members since you are sharing before making the decision as a leader or member. McInerney (2005) has suggested some of the business cases through practices in personnel decisions. For example, the quickness of staffing decisions. This is issue can be endured such as hiring, firing, positioning, bouncing and motivation issues. In this case, we may need to use teleconferencing, or decision support systems since the decision needs to be quick. At the end it is very reliable on the organization size and strategy. ‘Good decision making is based on preparation and routines of effective communication’ (McInerney, 2005: .27). Even though technologies have been available in various ways around the world, but we still need to enhance the communication skills in order to have a perfect knowledge sharing process. McInerney (2005) has proposed a diagram for organization learning process which will play a very important role to improve the knowledge sharing activities in the organization. The diagram shows the three functions of organizational learning Repositories, Active Knowledge Transfer and Decision Making Tools.
The next step in communication, employees will need to deliver their knowledge through communication styles. As McInerney (2005) mentioned earlier that communication is remaining very important factor even though technologies are available. Once the communication takes a place into the process, decision making methods will be in consideration based on the availability of decision making tools. The tools can expressed such as DSS, reports, knowledge management systems and collaboration tools (McInerney, 2005). Codification the decision analysis and development results will help the organization to have a repository of all the experiences, problems, limitations and results of any taken decision. The repository can contain reports about the organizational projects and issues. McInerney (2005) has tried to relate decision making with knowledge management via KS (Knowledge Sharing). Knowledge is carried everywhere, but people sometimes will have some difficulty to share their knowledge through the general meetings or discussions. That’s why it is much recommended for organizations to involve their employees with different positions and experiences into training programs. These training programs will be very useful for employees since it will be preparing them to be enrolled in decision making methods, and it also encourage them to communicate their ideas and suggestions with the fear of losing their knowledge (McInerney, 2005).
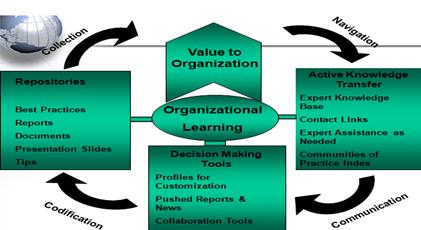
Figure 5: Organizational
Learning Framework. (Mcinerney, 2005)
Hansen et al (1999) have formulated knowledge management strategies into three stages Technological, Personalization and Socialization strategies. Technological strategy means to be the strategy which supports technology, database and explicit knowledge. Individuals will need to express their knowledge through explicit sources in order to have a record in the database. It also includes the networking and communication issues in the organization. Hansen et al (1999) have described the personalization strategy as follow it is more to be tacit knowledge since the person will demonstrate the knowledge through face-to-face dialogues and using communication skills. This strategy is meant to be established by human resource department since it is surrounded with people behaviors and actions. The last strategy which is the socialization strategy, it is however combination of technological and personalization strategies. For example some employees would exchange their knowledge through network or communities, and it will include some discussion and sharing ideas through communication process. Overall, these strategies can match with the knowledge management enablers. Knowledge enablers are Technology, Culture and Infrastructure. The technology is used as a tool to speed up the transfer of knowledge. It offers the information sources and it makes it easier for the employees to transfer knowledge in very effective way and very fast as well. That’s why many organizations are using technology nowadays to build their strategy in faster way and saving cost method. The second enabler which is culture, which is the ability to make people more motivated towards each other, it encourages them to share knowledge and take the advantage to lead as well. Infrastructure enabler is the most important enabler through this research. The research method will analyze people behaviors when they are involved in decision making techniques. Infrastructure is the basic environment of an organization, the structure of the organization and everything that surrounds the organization. It also includes the technologies offered within the organization, processes and the information flow in the organization. Even if the organization interacts with best technology available but people are not committed to do the job; then there will be no knowledge management environment (Hansen et al, 1999).
The Foundation Coalition (2001) has stated that decision
making should be practiced in well prepared environment. ‘An environment in
which everyone on the team feels comfortable in sharing his/her ideas and
proposing solutions raises the quality of the decisions’ (The Foundation
Coalition, 2001: 2). It was definition of the suitable environment for effective
decision making process in teams. The environment should be capable of
communication skills and conflict management. The employees should be trained
to improve the quality of their communication skills in order to have an
effective decision making process. The managers will have the responsibility of
managing the conflict of ideas among the employees, since conflicts may lead to
another new idea. The decision making environment can be called the thinking
environment, and there many factors under the thinking environment. ‘Everything
we do depend on the thinking we do first’ (Kline, 1999: 40). The first factor
was the active listening, employees should be aware of this issue since the
problem definition will be clear during active listening. It is also including
the ethical listening, employees will need to listen carefully and avoid
interpreting the speaker while presenting his/her opinion. The second factor is
incisive questions; incisive questions link the thinker with a good idea. The
employees will need to ask themselves several questions in order to create a
good idea. Equality is the third factor of the thinking environment. Employees
should ensure the equality between them, each member will be given his/her fair
time to analyze and explain your opinions and ideas. The managers or leaders
should manage the team in order to ensure equality between employees (Kline,
1999: 40).
Emotions should not be ignored during the discussion. Because
employees are also affected when their own opinions are ignored, this will
generate an upset feeling into them. The studies have proved that people will
be ineffective in decision making process when they are not emotionally
stabled. The information also plays an important role of the thinking
environment; insufficient information will lead to misleading solutions.
Employees will work much better if all the necessary information is provided by
the organization or leader. Employees will prefer working on something real,
real data and real facts; that’s why managers should have the notification of
the sufficiency of the information. The place to have decision making process
is also important due the psychology of employees, employees will prefer to
work in good place while they can concentrate, demonstrate and analyze their
ideas (Kline, 1999). There are also decision making tools such as
brainstorming, multi-voting, affinity grouping and prioritization matrix (The
Foundation Coalition, 2001). Decision
making situations are very important to the type of the decision. Even the
members should know their authority based on the situation. Ahmed (2008) has
also analyzed the decisions made by different managers. The lower and middle
managers will have the most programmed decisions, programmed decisions which
are routine situations for the organization. Programmed decisions will be
practiced everyday within the organization until the similar situations will be
solved by programmed decisions. On the other hand, the top managers will have
the highest amount of un-programmed decisions. These decisions are called
un-programmed decisions because they weren’t practiced among the organization
members. Critical and immediate decisions are usually un-programmed decisions
(Ahmed, 2008).
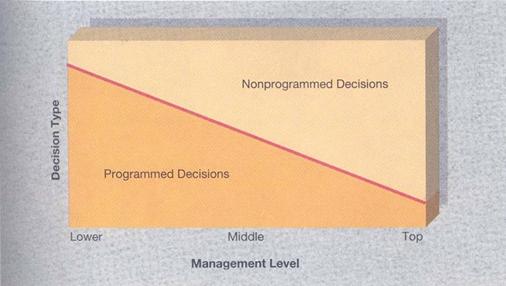
Figure 6: Decision Making Situation And Management Levels. (Ahmed, 2008)
3. Research Design
The research design will be relying on the data collection method. It consists of functions that can lead to the development of the research methodology. Kumar (2005) has perfectly defined the research design process, ‘It is a procedural plan that is adopted by the researcher to answer questions validly, objectively, accurately and economically’ (Kumar, 2005: 84). Therefore the research design is yet to be successful by succeeding the following factors, Validity, Objectivity, accuracy and Economic balance. In order to validate the collected data, the study should ensure that the instrument used could really answer the research questions; otherwise the instrument used for data collection has a low rate of validity. They study should consider the reliability of the data; the data should be realistic and proven.
Figure
7: Research Design
3.1. Data Collection Instrument
The research is investigating a various of decision making methods. In order to collect data that is related to decision making methods; this study will need to find people who are entitled and authorized for making decisions. Those people are usually managers. So to minimize the complexity rate of finding these people; this study will collect the data from anyone who has participated or witnessed decision making processes. Even different employees from different positions will be helpful since they can tell some cases or stories about their organizations strategies towards making decision.
3.2. Questionnaire
The questionnaire has been chosen as the data collection instrument. It is almost more economical since the questionnaire has been distributed through email. The best advantage of questionnaire is the ability to answer widely. In other words, questionnaire will contain open ended questions that lead to the research objectives. The questionnaire has three questions to be answered by the participants, and each question has a goal behind it to achieve the research objectives.
3.3. Sampling
In order to process with the questionnaire process, the study will need to select a sample method. There are 2 types of samples: random and non-random sampling. ‘Random sampling where only chance determines which items are selected. Non-random sampling is that the researcher deliberately selects the items to the sample’ (Routio, 2007). Judgmental or purposive sampling is the chosen method for this study. The Judgmental sampling is one of the non-random sampling methods. It is very useful to prove a concept or principle from the study. ‘The researcher only goes to those people who in his/her opinion are likely to have the required information and be willing to share it’ (Kumar, 2005: 179). The primary data is collected from 10 organizations from 5 countries.
The research is aiming to have people from different organizations with different cultures as well; it will also look into various industries to investigate on how the industry nature can play a role during decision making. Since the research focuses on knowledge management practices; so the research should investigate with people from different organizations and industries. The answers should be provided from individuals who work in different positions, because positions have different authorities to make a decision or to participate in decision making process.
4. Data Analysis
Respondent 1 has listened
to the concept of knowledge management after explaining and presenting for him
the idea of knowledge management activities. ‘Ummm,
yes as you said knowledge management is very affective for any organization,
and we will be glad to practice it in the nearest future. But for now, I think
we are quite capable of making decisions’. The research wants to know
recommendations to be suggested from Respondent 1 then he answered ‘Yes, I
would like to have a database or repository to have all the decisions made
previously so I can use it as a reference in similar situations, and yes, btw I
always organize activities every Friday to get the employees out of the routine
and to make sure that we satisfy their entertainment lifestyle as well.
Knowledge sharing is practiced here since we always sit together during having
coffee or tea and discuss about cultures and problems. As a HR manager, I care
about this stuff since it shows me the personality of the employees and how
they react towards business and personality issues’. Respondent 2 was not aware
about knowledge management concept, therefore he did not know how analyze the
use of knowledge management in her organization.
When Respondent 3 was asked about knowledge management, Respondent 3 replied ‘Yes, knowledge management is well known approach to strengthen the sharing process into organization. I always practice knowledge sharing during meetings with the team members; I always encourage them to through their ideas and suggestions on the table which might be useful anyhow. Plus, I always try to satisfy all of them by reaching the commitment point, I try my best to make everyone agrees with the decision. But as I said before, it depends on the time given, so if no enough time then I will have the final call’. Since repository was suggested to be involved in MDEC as referencing tool, she likes the idea by saying ’Yeah Yeah. I would love to have database for our previous decisions and operations in order to save time and have collective repository. By the way, our new employees are required to present their tasks in the earlier months of joining MDEC, it is considered as a good step from MDEC to get the employees familiar with knowledge sharing environment; and to start coping with MDEC culture’. When the question came about knowledge management, Respondent 4 seems like she doesn’t understand what are knowledge management tools, and she answered ’The analyst will have numbers of whom working under the Fund to ask them any question when the analyst finds some issues. The analyst also, can visit that company or the location of the Fund to have clear vision on the project they are going to joint’.
When
Respondent 5 was asked about the knowledge management tools provided in the
organization, she said ‘The tools may vary based on each case, but surely all
strategy and actions will be discussed internally between 3 people (me and 2
other colleagues, who are located in Surabaya and Dubai). Three of us are
basically running the business as we are designated to handle different region,
all decision made after discussion among us and one case can be used to apply
to other case in other country. Some cases we even do trial and error planning
and implementation, as we have limited human sources to handle and at the same
time we are force to work in fast environment where sometimes decision has to
be made on the spot while negotiating with customers. However if the case is
involving financial issue such as huge investment or funding, I have to wait
for approval from board of directors in Dubai before proceeding. Similar case
if there is an inquiry from customers to have credit in payments, and then I
have no authority to provide unless I have approval from directors’.
Respondent
6 added ‘We offer our employees the
necessary training in the respective discipline for decision making skills so
that the employee can take necessary decisions with in his/ her own purview. On
the job training is more imparted for valuable decision making. Apart from the
above, selective guidance can be obtained or called for from any senior member
of the management by the employee’. Respondent 7 indentified the
training sources ‘Our Company is certified by ISO9001, ISO22000, HACCP and GMP.
We also have Halal and Kosher certificates. Any
decision must be followed by a reason. Even at the TOP Management decision was
making such as for PROJECTS; the decision to be made from the Board of
Directors meeting’.
Respondent
8 was asked about the knowledge management tools and techniques, he answers ‘I
believe there is no strict answer for that. It depends on many aspects, like
form of company/institution, business nature, human resources, etc. In my
institution, most of research staffs came from various educational backgrounds
and experiences. They have expertise in specific fields like sociology,
anthropology, politics, economics, environment science, etc. That is why
discussions are very important thing to do, to gather various ideas from
various backgrounds in order to get comprehensive and high quality of research result’.
Respondent 9 explained ‘Cement Australia provides training in and encourages
the use of decision making tools including Kepner Tregoe and PMA. Working groups often use these tools to
keep a project’s decision making on track and ensure the desired outcome is
reached’.
Respondent 10 also had mentioned
the tools, techniques that the organization uses ‘the
development of staff capacity at the decision representations requires the
following:
·
Development of
special departments of human development in the institutions under the
responsibility staff qualifiers and specialists in the fields of Human
Resources Management that will prepare and qualify the cadres in line with
current developments in the areas of workforce human.
·
Develop plans
for the Foundation includes the organization of practical sessions of training
for staff based on competencies whether local or foreign industries specialized.
·
To allocate its annual budget institutions in
the reliability of financial assistance for research and development studies
for the rehabilitation and training of staff.
· The development of policies, plans and programs of the institution to accommodate the staff scholarship abroad to enroll in specialized courses in institutions, colleges and universities developed to achieve the process of acquiring and exchanging expertise in the areas of quality skill development of professional capacity.
·
The focus is in the process of
building staff to ensure compatibility and harmony between the inputs and the
rehabilitation of staff requirements and development outcomes at the
intermediate level long-term.
·
To put the
institutions involved in the plans and programs of the margin of the right to
sign agreements of cooperation and exchange of experiences with peer
institutions with pilot experiments in the same field of work, whether at home
or abroad’.
The research will generate comparisons between the different data provided by the respondents. The first table will show the data provided from the respondents regarding the decision making methods practiced in their organizations. This table will aim to summarize the how the 10 respondents establish decisions in the organization, and what models they use. Table 2 shows the factors that may affect the process of decision making. Table 3 shows the differences between the knowledge management activities practiced in the different organizations of the respondents:
Table 1: Data Processing For Decision Making
Methods
|
Question |
Data
Provided |
|
-
What
are the methods used in the organization for Decision Making? |
·
Consensus,
Majority group decision. ·
Strategic
and Tactical Decisions made by the top management. ·
Group
decision making based on Voting and discussion. ·
Operational/unit
level is given authorities to make decisions in limited rage. ·
For
some important decision, the last cal is for the top management. ·
Based
on averaging individuals opinions and experts group decision making. ·
Decisions
based on the nature of business. ·
Assisting
the top management to have the best decision. ·
Immediate
and fast decisions. ·
Analyzing
the information before making the decision ·
Systematic
decision making approach. ·
Strategic
model. ·
Full
commitment. ·
Policies
and rules may limit the decision efficiency. ·
Consultation
with experts and middle managers. ·
Group
decision making is more preferred to save time and for good quality decision |
Table 2: Data Processing For Decision Making
Factors
|
Question |
Data
Provided |
|
-
What
are the factors that may affect decision making process? |
·
Business
nature. ·
Organization
culture. ·
Position
responsibilities. ·
Experiences. ·
Employees’
commitment. ·
Organization
history. ·
Emergency
of the task/operation. ·
Types
of decision level (tactical, strategic, and operational). ·
Country
culture/regulation |
Table 3: Data Processing For Knowledge Management
Activities
|
Question |
Data Provided |
|
-
What
are the knowledge management activities practiced in
the organization? |
·
Knowledge
sharing. ·
Supportive
for new ideas and suggestions. ·
Motivation
from top management. ·
Organization
networks. ·
Organization
culture. ·
Professional
certificates and training sessions are very useful. ·
Guidelines
to ease the decision making process for employees. ·
Technology
Tools. ·
Leadership
and Communication Skills. ·
Repository
Practices. |
5. Findings
This is the last phase of the project since it is going to list all the findings during the literature review and research methodology. The findings can be parted into three categories: Decision Making Models, Knowledge Management activities and Decision Making Factors.
5.1. Decision Making Models
The literature review process has explored the decision making models, methods and techniques. The research could identify the decision making levels as well, which are: Operational, Strategic and tactical. All the decisions should be practiced based on these levels. Usually operational decisions are meant for business units, strategic decisions held by top managers and stakeholders, tactical decisions handed by middle and top managers. Here is the list of all the models that have been explored through decision making as shown in Table 1:
·
Business
Decision-Making: this model will involve some steps in analyzing the available
information through the group discussion; each business unit is given some
authorities to take the decision as well. The business model consists of
several methods:
-
Operational
level decisions -
Following Policies and Rules
-
Business
Nature -
Information Analysis
-
Consultation
with managers and experts
·
Systematic
Decision Making: is a systematic approach aims to construct the organization
environment to cope with the employees’ activities, members will need to
discuss their solutions with each other and analyze all the possible solutions
to achieve the best one. The systematic model consists of several methods:
-
Group
Decision Based on Discussion -
Business Nature
-
Information Analysis
·
The CCVC Methods: can be used to ensure consensus through the
employees, and also to ensure the full commitment factor since all the methods
are practiced through group of members. The CCVC model consists of several
methods:
-
Consensus,
majority group decision -
Voting and Discussion
-
Sometimes,
last call for top Management -
Fast Decisions
-
Full
Commitment -
Consultation
-
Group
Decision Making for high quality decisions
·
Scientific
Decision-Making Framework: is a model that focuses on the health industry,
therefore members should collect and analyze the information very carefully
before preceding any decision. The Scientific model consists of several
methods:
-
Consultation
with managers and experts -
Strategic Options
-
Following
Policies and Rules -
Information Analysis
·
Strategic
Decision-Making Framework: this model is meant to be practiced by the top
managers or stakeholders, it involves strategic and tactic decisions that may
affect the organization. The Strategic model consists of several methods:
-
Strategic
and tactical decisions by top Management -
Strategic Options
-
Assisting
the top management to have the best decision
·
Team
Decision-Making Methods: the methods are combining several actions and
activities to be involved in group decision making, the main purpose of group
decision making is to achieve the consensus stage which is the full commitment
point. The Strategic model consists of several methods:
-
Consultation
with managers and experts - Voting and Discussion
-
Consensus,
majority group decision -
Opinions Averaging
-
High
Quality Decisions
5.2. Decision Making Factors
After analyzing how knowledge management activities can add value to decision making process; it was recommended to look into the factors that may affect decision making. During the interviews and questionnaires, the study could observe the factors that play roles towards the efficiency of making decisions. Here are the factors of decision making methods:
· Business nature.
· Organization culture.
· Position responsibilities.
· Experiences.
· Employees’ commitment.
· Organization history.
· Emergency of the task/operation.
· Types of decision level (tactical, strategic, and operational).
·
Country culture/regulation
5.3. Knowledge Management Activities
· Knowledge sharing
· Supportive for new ideas and suggestions
· Motivation from top management
· Organization networks
· Organization Culture
· Technology Tools.
· Repository Practices.
· Professional certificates and training sessions
· Leadership and Communication Skills
· Guidelines to ease the decision making process
During the data collection process, the primary sources such as interviews and questionnaires have supported this study in figuring out how companies have the willingness to ease the decision making process. Knowledge management is considered new term, that’s why it was ideal to look through the participants’ answers in order to observe how knowledge management activities are practiced through the organizations. The research could observe that most of the organizations rely on technology in the first phase rather than socializing and communication skills development. Here are some of the knowledge management activities that have been practiced to improve the efficiency of decision making process:
5.4. Decision-Making Framework Supported by KM
Activities
The research aims to establish decision making framework supported by knowledge management activities. It is the main objective of this research since it will combine some of the models discovered during the literature review, and enhance it with knowledge management activities. The framework will combine 2 of decision making models: Business Decision Making (Bowett, 2009) and Systematic Decision Making (MindTools, 2010). In addition, the framework will also include the decision making methods for leadership skills that were proposed by (Patterson et al, 2002). The second part of the framework will be the knowledge management activities that may affect the steps during decision making mechanism. The figure below will demonstrate the combination between Business and Systematic Decision Making models:

Figure
8: Adopted Decision Making Model. (Bowett, 2009) & (Mindtools,
2010)
In addition, the research will demonstrate how knowledge management activities can be applied into these decision making stages:
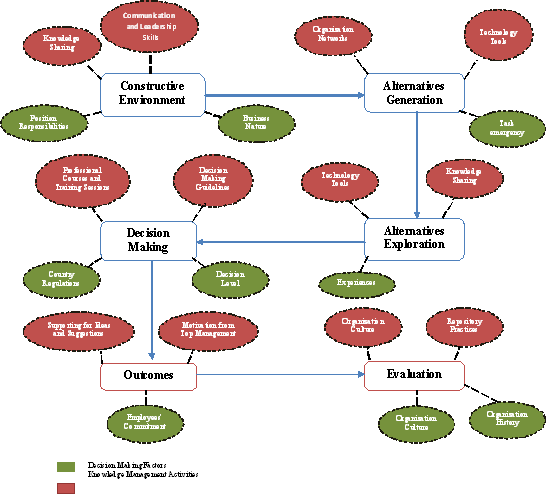
Figure
9: Decision Making Model Supported
By KM Activities (Bowett, 2009) & (Mindtools, 2010)
6. References
Ahmed, Q. (2008). Managerial Decision Making. [PowerPoint presentation], [Online], Available:
http://www.slideshare.net/greatqadirgee4u/managerial-decision-making
[20 December 2010].
Akhter, F. (2010) Effect of emotions on Human behavior and rational decision making, [Online], Available: http://www.articlesbase.com/self-help-articles/effect-of-emotions-on-human-behavior-and-rational-decision-making-2170823.html [15 November 2010].
Bellinger, G. (2001). Knowledge management-emerging perspectives, Systems Thinking, [Online], Available: http://www.systems-thinking.org/kmgmt/kmgmt.htm [28 October 2010].
Bowett, R. (2009)
Decision making in business, [Online], Available: http://tutor2u.net/business/organisation/decisionmaking.htm
[4 November 2010].
Briely, D. (2007) The effects of culture on
decision making and judgment,
CiteMan Network. (2008) Primary and secondary data, [Online], Available: http://www.citeman.com/3929-primary-and-secondary-data-2/ [3 December 2010].
Cremer, D., Dick, R., Tenbrunsel, A., Pillutla, m., and Murnighan, J. (2010) ‘Understanding ethical behavior and decision making in management: a behavioral business ethics approach’, Journal of Business Ethics, pp. 5-6.
Hansen, M.T., Nohria, N. and Tierney, T. (1999) ‘What is your strategy for managing knowledge’, Harvard Business Review, pp. 8-11.
Haroon, F. (2007). Role of knowledge management in the decision making process. [PowerPoint
presentation],
[Online], Available:
http://www.slideshare.net/haroones007/role-of-knowledge-management-in-the-decision-making-presentation
[22 December 2010].
Health Canada, (2010) Decision making framework, Ottawa: Canada Science and Research Office, [Online], Available: http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/sr-sr/advice-avis/decision/index-eng.php [10 December 2010].
Hilton, B. (2008). Archive for Determinants of Organizational Culture. Organizational Climate, [Online], Available: http//organizationalclimate.wordpress.com/category/determinants-of-organizational-culture/ [19 January 2011].
InfoEdge. (2006) Build a strategic decision making framework,
[Online], Available: www.infoedge.com/samples/in-6002sam.pdf
[5 January 2011].
Johnson, D.W., Johnson, R.T., and Holubec, E.J. (1993) Circles of
learning: Cooperation in the classroom,
Edina: Interaction Book Co.
Kim, S. K., Lim, S., and Mitchell, R. B. (2004) Building a knowledge model: a decision-making approach, [Online], Available: http://www.tlainc.com/articl68.htm [25 October 2010].
Kline, N. (1999) Time to think Listening to ignite the human mind, London: Ward Lock Wellington House.
Kumar, R. (2005) Research methodology:
A step-by-step guide for beginners, London: SAGE Publications Inc.
Markman, A. (2010). Culture and decision making.
McInerney, R. (2005). What happens when decisions must be made quickly. [PowerPoint presentation], [Online], Available: http://www.comminfo.rutgers.edu/~clairemc/Darmstadt.Anniversary.ppt [21 December 2010].
Mind Tools Community. (2010) Introduction
to decision making techniques: A systematic Approach to decision making,
[Online], Available: http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTED_00.htm [8
November 2010].
Patterson, K., Grenny,
J., McMillan, R., Switzler, A., and Covey, S. (2002) Crucial conversations: tools for talking when
stakes are high, New York: McGraw-Hill.
Routio, P. (2007) Sampling, [Online], Available: http://www2.uiah.fi/projects/metodi/152.htm [2 December 2010].
The Foundation Coalition. (2001) Effective decision making in teams, [Online], Available: http://www.foundationcoalition.org/teams [17 November 2010].
United Nations (UN), (2001) Knowledge management for
decision-making: tools, institutions and paradigms, Addis Ababa: Economic
and Social Council: Economic Commission for Africa.
Contact the Authors:
Marwan Hesham Noman, Multimedia University, Malaysia
Email: Marwan2002us@yahoo.com
Azira Abd Aziz, Multimedia
University, Malaysia
Email: azira@mmu.edu.my